Are you eager to uncover the secrets of manufacturing excellence? Do you ponder the best processes for creating intricate, high-quality metal components? Worry not, as you’ve spotted the perfect place! This write-up will explore everything under the sun of Low-Pressure Die Casting, a revolutionary technique reshaping modern manufacturing.
Whether in the automotive, aerospace, or precision engineering industries, this method could be your game-changer. Wanna adopt the future of metal component manufacturing with us? Let’s get started!
The Fundamentals of Low-Pressure Die Casting
What is Low Pressure Die Casting?
Low-pressure die casting is a metal casting method where molten metal is injected into a mold cavity using low pressure, usually between 10 to 100 psi. This pressure is much lower compared to regular die casting. Though it’s a slower process, low-pressure die casting creates castings with smooth surfaces and precise dimensions.
How Low-pressure Die Casting Works?
Low-Pressure Die Casting is a sophisticated metal casting technique that combines ingenuity with precision to create intricately shaped components. The process is based on a straightforward principle: using low pressure to fill the mold with molten metal, ensuring a controlled and reliable casting.
Steps Involved in Low-Pressure Die Casting
Here is the step-by-step process of Low-Pressure Die Casting:
- Preparation: The process begins with meticulous preparation. A reusable metal mold, also known as a die, is carefully cleaned and coated with a release agent to facilitate easy removal of the casting after solidification. Additionally, the sprue and runners, which act as channels for the molten metal, are attached to the die.
- Clamping: The mold is securely clamped using a hydraulic system, creating a closed chamber for the casting process.
- Degassing: Before introducing the molten metal, any trapped gases within the mold are removed through a degassing process. It ensures the casting remains porosity-free, improving structural integrity.
- Metal Injection: The heart of Low-Pressure Die Casting lies in the controlled injection of molten metal into the mold. A furnace holds the metal at its melting point, and a ceramic tube, called a riser tube, is immersed in the metal. The pressure within the furnace forces the metal up the riser tube and into the die cavity at low pressure, typically ranging from 0.7 to 1.4 bar.
- Solidification: Once the mold is filled, the molten metal is left to solidify within the die cavity. The cooling time varies based on the complexity and size of the component.
- Ejection: After the metal has solidified, the clamping mechanism is released, and the die opens. Ejection pins or mechanical devices gently push the casting out of the mold.
- Trimming and Finishing: The casting may undergo additional trimming and finishing processes to remove excess material, refine the surface, and ensure the final product meets the desired specifications.
Through precise execution, Low-Pressure Die Casting delivers castings with flawless surfaces and accurate measurements, cementing its position as a preferred approach in producing top-notch metal components.
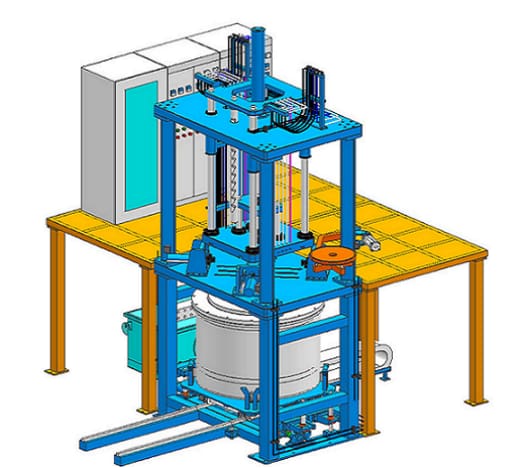
Machinery and Equipment Used in LPDC
The effectiveness of Low-Pressure Die Casting heavily depends on specialized machinery and equipment specifically designed to execute the process with precision and efficiency.
- Low-Pressure Furnace: This crucial component holds and melts the metal at the required temperature. It ensures consistent metal properties and optimal casting results by operating under controlled conditions.
- Die Casting Machine: Responsible for clamping the mold, injecting the molten metal, and applying low pressure during casting. It operates with precision to achieve uniform and reliable castings.
- Riser Tube Assembly: An integral part of the metal injection system, the riser tube helps control the flow of molten metal into the die cavity at the desired low pressure, contributing to the formation of defect-free components.
Role of Molds and Patterns
In the Low-Pressure Die Casting process, molds and patterns are crucial in creating intricate and accurate components. Let’s delve into their significance and functions:
Molds
Molds, or dies, are crafted from high-quality materials like steel or alloys. These molds replicate the exact shape and features of the desired component. The molds endure high temperatures and pressures, ensuring consistent dimensions and surface finishes in the final product during the casting process. Molds withstand the repetitive nature of the casting process and are critical to the success of Low-Pressure Die Casting.
Patterns
Patterns serve as master templates for creating molds. They precisely represent the final component’s shape and dimensions, allowing for the creation of accurate impressions within the mold. Patterns are essential in ensuring each casting produced through the Low-Pressure Die Casting process maintains the required specifications and conforms to the design standards. The precision of patterns directly influences the quality and integrity of the final components.
In-depth knowledge of specialized machinery, molds, and patterns provides invaluable insights into the intricacies of Low-Pressure Die Casting. Its capacity to deliver precision and top-tier components make it pivotal in modern manufacturing, perfectly aligned with the diverse requirements of various industries.
What Types of Materials Are Used in Low-Pressure Die Casting?
Suitable Materials for LPDC
Low-Pressure Die Casting offers a range of materials suitable for various industrial needs. Let’s explore common materials and their specific applications and advantages:
-
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are widely used in Low-Pressure Die Casting due to their lightness, corrosion resistance, and impressive strength-to-weight ratio. They find ideal applications in automotive, aerospace, heat exchangers, and electronic housings thanks to their excellent thermal conductivity.
-
Magnesium Alloys
Magnesium alloys are popular in Low-Pressure Die Casting because of their low density, making them perfect for lightweight automotive and aerospace applications. They provide high-impact strength and good dimensional stability, enhancing the overall performance of the end product.
-
Copper Alloys
Copper alloys are well-suited for electrical and thermal conductivity applications. They find use in producing electrical connectors, heat sinks, and components for power transmission.
-
Zinc Alloys
Zinc alloys boast exceptional casting abilities and affordability, making them a favored choice for crafting intricate components in industries like automotive and electronics.
-
Other Alloys
Low-Pressure Die Casting can also utilize alloys like brass and bronze, depending on specific application requirements. These alloys offer distinct properties that can be helpful in specialized industries and applications.
Material Properties for Different Applications
In Low-Pressure Die Casting, material selection can impact performance and cost-effectiveness. The choice of materials shapes modern manufacturing and meets industrial needs. Let’s compare material properties for different applications:
-
Strength and Stiffness
Renowned for their exceptional strength and stiffness, aluminum and magnesium alloys find extensive use in the automotive and aerospace industries as essential structural components.
-
Corrosion Resistance
Aluminum alloys and stainless steel are ideal for components exposed to harsh conditions, as they offer excellent corrosion resistance.
-
Thermal Conductivity
The exceptional thermal conductivity of copper alloys makes them perfect choices for heat transfer applications, including heat exchangers and cooling systems.
-
Weight Considerations
The low density and lightweight characteristics of magnesium and aluminum alloys make them highly sought-after for achieving weight reduction goals in various industries.
By thoroughly analyzing material characteristics, you can fine-tune Low-Pressure Die Casting for precise applications, yielding superior components that satisfy the exacting needs of present-day industries.
Low-Pressure Die Casting Vs. Other Die Casting Methods
In the world of die casting, several other methods vie for attention, each offering unique strengths and applications.
-
High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is a casting process that utilizes high pressure to inject molten metal into the mold cavity. It is particularly proficient in the rapid production of lightweight and intricate parts.
-
Gravity Die Casting
Gravity Die Casting uses gravity for mold filling with molten metal. It’s simple and cost-effective, great for making larger and thicker parts. However, it may not be as precise as Low-Pressure Die Casting for complex and detailed components.
Advantages of Low-Pressure Die Casting over Other Methods
-
Reduced Porosity
A standout advantage of Low-Pressure Die Casting is its ability to minimize porosity in casted components. Controlled injection at low pressure reduces air pockets, creating denser and more reliable castings. This improvement in structural integrity leads to components with superior mechanical properties, meeting superb standards.
-
Improved Quality and Mechanical Properties
Low-Pressure Die Casting excels in exceptional surface finishes and dimensional accuracy. The controlled filling process ensures smooth flow into intricate details, creating precise and finely crafted parts. Reduced porosity enhances mechanical properties, such as higher tensile strength and fatigue resistance, making it an excellent choice for critical components.
-
Cost-Effectiveness
Low-Pressure Die Casting may require specialized machinery and molds, but it is cost-effective in the long run. Producing top-quality components with minimal defects reduces rework and scrap, leading to higher yields and cost savings. Moreover, the ability to produce complex shapes and thin-walled parts with precision can save materials and lower overall production costs.
By leveraging these advantages, Low-Pressure Die Casting emerges as a preferred method for manufacturing high-quality metal components with intricate designs, meeting the demands of diverse industries and pushing the boundaries of modern manufacturing.
Future Trends and Innovations in Low-Pressure Die Casting
Predicting Upcoming Trends
The advancements in Low-Pressure Die Casting may impact various industries and shape the future of manufacturing. Let’s explore some key trends that are set to revolutionize the industry:
-
Advanced Automation
Robotics and AI will play a significant role in enhancing process control and productivity in Low-Pressure Die Casting. Real-time data analysis will enable predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and optimizing efficiency.
-
Materials Innovation
Ongoing research and development will uncover novel alloys and composites with enhanced properties. These advancements will yield materials boasting improved strength, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance, broadening the scope for innovative component designs.
-
Digital Twin Technology
The adoption of digital twin technology will optimize Low-Pressure Die Casting production processes. Virtual representations of the casting process will allow manufacturers to simulate and analyze various scenarios, leading to more efficient production and reduced time-to-market.
-
Sustainable Practices
Environmental concerns will drive the implementation of more energy-efficient and eco-friendly casting methods. Low-Pressure Die Casting aligns well with the growing focus on sustainability, minimizing waste, and producing top-notch components.
-
Integration of Additive Manufacturing
Integrating 3D printing and Low-Pressure Die Casting will open new possibilities for component designs and customization. By combining these technologies, manufacturers can create complex and unique parts that were previously challenging to produce through traditional methods.
Shaping the Future
As these trends continue to evolve, Low-Pressure Die Casting will influence various industries in some profound ways.
-
Automotive and Aerospace
The ability to produce lightweight and efficient components through Low-Pressure Die Casting will improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions in the automotive and aerospace sectors.
-
Electronics and Renewable Energy
Low-Pressure Die Casting will help manufacture top-notch heat sinks and components for renewable energy systems like wind and solar. These components will foster greener and more energy-efficient electronics and renewable energy technologies.
-
Medical and Healthcare
Intricate and precise medical devices and implants will be manufactured using Low-Pressure Die Casting, catering to the growing demand for personalized healthcare solutions.
-
Advanced Machinery
Innovations in machinery and automation for Low-Pressure Die Casting will enhance industrial efficiency across various sectors, leading to streamlined production processes and cost savings.
Conclusion
Low-Pressure Die Casting is a crucial process in manufacturing. In this article, we learned about the basics of Low-Pressure Die Casting, the materials used, quality control, and automation. This technique has revolutionized how we make precise parts. Manufacturers can stay competitive, meet efficiency and sustainability demands, and produce excellent products using Low-Pressure Die Casting. Let’s embrace innovation and technology to improve manufacturing with Low-Pressure Die Casting.